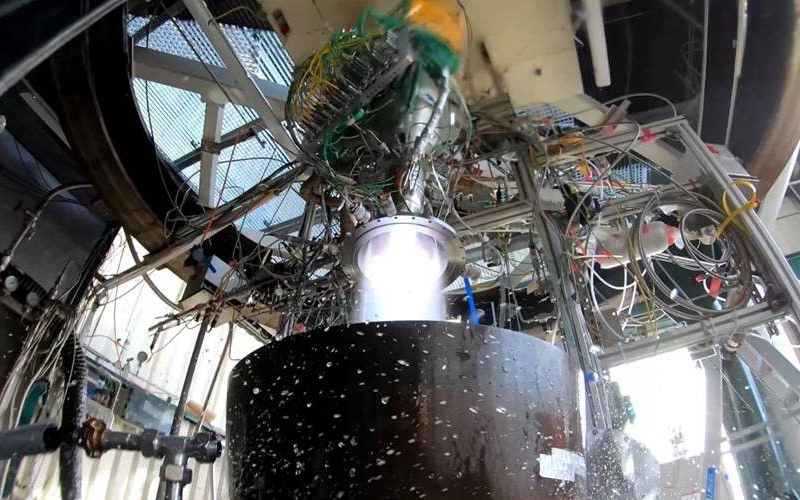
An ESA-led Test Review Board has signed off on a hot fire test campaign of an engine being developed by ArianeGroup for the European Argonaut lunar lander.
First called the European Large Logistic Lander (EL3), Argonaut is designed to be a multi-use lunar lander capable of carrying payloads of between 1,500 and 1,800 kilograms to the surface of the Moon. The development of Argonaut was approved by ESA member states during the agency’s ministerial council meeting in late 2022.
The SPE-T (Space Propulsion Engine – Throttleable) engine is based on the BERTA engine demonstrator, which was developed under the ESA Future Launchers Preparatory Programme and test-fired for the first time in early 2019. A version of the SPE rocket engine will power the Ariane 6 Astris kick stage, which is currently being developed by ArianeGroup.
According to a paper presented at the tenth edition of the Aerospace Europe Conference in 2023, the ArianeGroup SPE-T engine is being considered to serve as the main engine of the Argonaut lunar lander. Other engines under consideration include the 6 kN RELIANCE engine from Nammo.
In a 24 June update on LinkedIn, ArianeGroup announced that it had completed a hot fire test campaign of a pre-development model of the engine utilizing hypergolic propellants. The flight version of the engine will utilize green propellants. The campaign included 1,450 seconds of testing covering a thrust range of between 2.7 and 5.9 kN. This test campaign was completed at the end of 2023.
Since then, a thorough analysis of the test data has been completed. As of yesterday’s announcement, the success of the test campaign has been formally confirmed by a Test Review Board that was led by the European Space Agency.




